Folate status in pregnancy is a critical factor for proper foetal development.
Humans cannot synthesise folate and pregnant women do not consume adequate quantities of it through their diet, therefore folate supplementation is required to prevent NTDs (neural tube defects) and is established by several Health Authorities (i.e. FDA, EFSA).
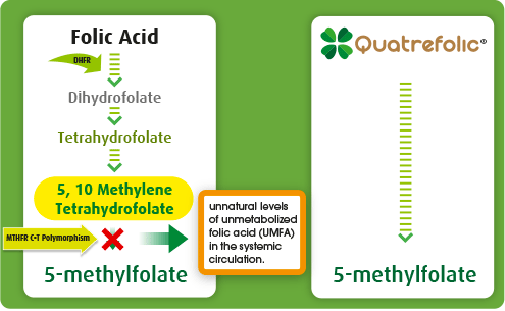
Folic acid is not biologically active and needs to be converted into the metabolically active 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) through a multi-steps process where the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) has a key role.
Some individuals, due to their unique genetic pattern of gene expression, have polymorphic forms of this enzyme and do not produce adequate or effective MTHFR.
Quatrefolic is structurally analogous to the reduced and active form of folate so it completely bypasses the damaged MTHFR conversion step and delivers a finished folate the body can immediately use without any kind of metabolisation.
Although the current recommendation implies women with MTHFR polymorphism may take a high dose of folic acid, they may not benefit from folic acid at a higher dose.
High doses of folic acid has also been found to mask B-12 deficiency and several studies have reported an increase in serum of unmetabolised folic acid (UMFA) levels with possible concerns about its potential overdosing and adverse effects.
Quatrefolic produces the metabolically active form of folate, even when the gastrointestinal pH is altered
Quatrefolic:
- Normally the only species found in circulation
- Usually transported into peripheral tissues to be used for cellular metabolism
- It is the only form able to cross the BBB (Blood Brain Barrier)
- Bioavailability is not affected by multi-steps process of conversion and by metabolic defects typical of folic acid and food folate, such as the polymorphism of the enzyme MTHFR (methyltetrahydrofolate reductase)
In fact, some individuals due to their unique genetic patterns and expression, have a polymorphic form of this enzyme and do not produce adequate or effective forms of it, with impaired folate metabolism and with exacerbation of folate deficiency.

