The vitamin E family consists of eight chemically distinct compounds: four tocopherols and four tocotrienols (alpha-, beta-, gamma- and delta-).
Tocotrienols differ structurally from tocopherols by the presence of three double bonds in their sidechain, which provides flexibility and enables these molecules to efficiently penetrate cell membranes, resulting in a more uniform distribution.
This delivers superior antioxidant and unique health benefits compared with regular vitamin E (tocopherol), such as maintaining brain and heart health. These distinct health properties of tocotrienols have gained significant attention in both the scientific community and also among manufacturers and consumers.
Vitamin E tocotrienols are scarce in nature. Oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) is the richest source of tocotrienols, with a content of up to 800 mg/kg (800 ppm). However, the recommended daily intake of tocotrienols is 30–50 mg/day for general wellness.
This equates to a dosage of approximately 37.5–62.5 g of crude palm oil per day, which is practically impossible to achieve via the diet, especially for the elderly. Therefore, the incorporation of tocotrienols through dietary supplements or functional foods and beverages is highly recommended.
Vitamin E requirement: high in the elderly
When compared with young adults of the same height, weight and level of activity, older adults have a lower energy intake requirement; but, the need for micronutrients such as vitamin E remains high.
However, reduced food consumption among the elderly results in lower nutrient intakes, which, with time, may lead to an increased risk of nutrient-deficiency associated diseases. In terms of vitamin E intake, alarming statistics of approximately 93% (females) and 88% (males) older than 50 were found to consume below the estimated average requirement of vitamin E by NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey).
This may indicate that the elderly population are jeopardising their health, as inadequate vitamin E intake could increase the risks of age-associated health conditions. As such, it’s time to shine a spotlight on vitamin E and, in particular, vitamin E tocotrienols — vitamin E compounds that have been scientifically proven to exhibit distinct health benefits that are not available from vitamin E tocopherols.
Bioenhanced tocotrienol complex
As with any of the fat-soluble vitamins, the oral absorption of tocotrienols is highly dependent on the type and amount of dietary fats consumed during ingestion. The absorption into plasma — or bioavailability — of tocotrienols also requires the secretion of bile and emulsification in the small intestine.
Additionally, the absolute oral bioavailability of alpha-, gamma- and delta-tocotrienol has been reported to be low and erratic, at 27.7%, 9.1% and 8.5%, respectively.
EVNol SupraBio, a patented, bioenhanced self-emulsifying delivery system that ensures the increased and consistent absorption of each individual tocotrienol into human plasma by up to 300%, compared with a regular tocotrienol oil extract, is the only tocotrienol complex in the market to have an actual human tissue distribution study, wherein the tocotrienols are proven to accumulate in vital human organs such as the brain and heart.
As a matter of fact, EVNol SupraBio has been used in many clinical studies to support brain (cognitive function, attenuation of white matter lesions and post-stroke protection) and heart health (healthy cholesterol levels, maintains arterial compliance and mitigates arteriosclerosis).
Brain health (neuroprotection)
Nearly three quarters of all strokes occur in people older than 65. The risk of having a stroke more than doubles each decade after the age of 55. Stroke or cerebral small blood vessel disease occurs when blood flow to the brain is obstructed, leading to the death of brain cells.
Studies have linked the presence of age-related white matter lesions to increased risks of neurodegenerative disorders such as stroke, cognitive impairment and dementia. The following White Matter Lesion (WML) study shows the brain protection effect of a natural mixed-tocotrienol compound.
Precerebral small vessel disease: In a randomised, double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial, 121 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)-confirmed WML subjects received bioenhanced palm tocotrienol complex (EVNol SupraBio) or a placebo for 24 months.
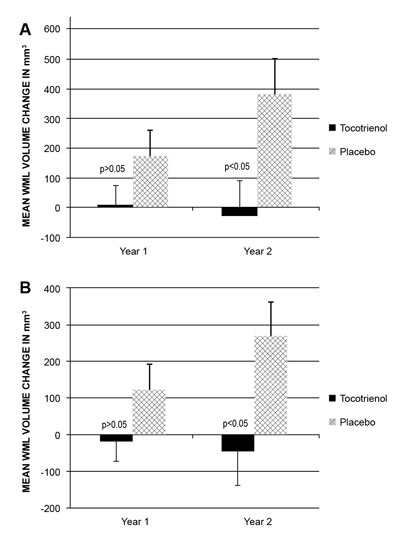
Figure 1: Mean WML volume change
In the placebo group, the mean WML volume increased by a statistically significant amount. In the treatment group, the mean WML volume remained unchanged (Figure 1). This is the first published clinical trial that shows that tocotrienols could potentially attenuate the progression of WML.
Post-cerebral small vessel disease: Conducted at the Ohio State University Medical Center, 20 mongrel canines were randomised into two treatment groups: bioenhanced palm tocotrienol complex (EVNol SupraBio) and vitamin E-deficient corn oil (control) for 10 weeks.
When compared with the control, the EVNol SupraBio-supplemented canines showed 20% and 40% reduced stroke-induced lesion volumes at the first and 24th hour, a higher relative connectivity of white matter fibre tracts, improved cerebrovascular collateral circulation and the increased expression of proarteriogenic (new blood vessels formation) genes.
As such, natural palm mixed-tocotrienol supplementation may reduce cerebral small vessel disease in a preclinical setting.
Nanomolar (10-9) concentrations of alpha-tocotrienol resulted in the complete recovery of neurons (meaningful neuroprotection) even when alpha-tocotrienol was introduced several hours after glutamate-induced toxicity.
NIH (National Institutes of Health)-funded studies have demonstrated that tocotrienols exert neuroprotection via five identified mechanisms that modulate neuronal cell death or survival:
- reduction in c-Src kinase activation
- inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase phosphorylation
- inhibition of phospholipase A2
- up-regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1)
- rescued stroke-induced loss of microRNA-29b and minimised lesion size.
In terms of cognition support, four large epidemiological studies conducted by researchers at the Karolinska Institute, Sweden, and Perugia University, Italy, show that Vitamin E Complete (a full spectrum of tocotrienols and tocopherols) reduces the risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in elderly Europeans.
When compared with cognitively normal people, AD and MCI subjects demonstrated significantly lower levels of total tocotrienols, total tocopherols and total vitamin E. Hence, low plasma levels of tocotrienols and tocopherols are strongly linked to AD and MCI, with tocotrienols having a stronger inverse correlation compared with tocopherols.
Heart health (cardioprotection)
An estimated 85.6 million American adults have one or more types of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Of these, 43.7 million (more than half of the affected population) are estimated to be older than 60.
About two thirds of CVD deaths occur in people age 75 and older. Furthermore, the almost 49 million people living with CVD in the EU cost the healthcare system up to €210 billion a year.
Cholesterol: In a clinical trial, hypercholesterolaemic subjects were randomly assigned to consume either EVNol SupraBio or placebo capsules daily for 6 months. When compared with the placebo, the EVNol SupraBio group showed significant reductions of total cholesterol and LDL-C by the fourth month.
Total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol levels continued to fall during the fifth and sixth month of supplementation. In conclusion, supplementation with palm mixed-tocotrienol shows healthy cholesterol level/lipid profile regulation.
Arterial Compliance: 36 healthy males were randomised to receive daily supplementation of 50, 100 and 200 mg of EVNol SupraBio or a placebo for 2 months. The 100 and 200 mg EVNol SupraBio groups demonstrated a significant reduction in augmentation index (AI), whereas all the EVNol SupraBio groups showed a significant decreased in pulse wave velocity (PUV).
Decreased AI and PUV values are strongly associated with arterial compliance (reduced arterial stiffness).
In addition, another important clinical trial conducted at the Kenneth Jordan Heart Foundation showed that supplementation with palm tocotrienol complex at 240 mg/day for 6 months mitigated arteriosclerosis in 92% of patients diagnosed with carotid stenosis (narrowing of the carotid artery).
By contrast, none of the patients receiving the placebo showed atherosclerotic mitigation, and 40% showed progressive disease. This study underscores the importance of palm tocotrienol complex in promoting heart health.
In a nutshell
EVNol SupraBio has been clinically proven to promote brain (WML attenuation and cognitive support) and heart health (healthy lipid profile and arterial compliance maintenance). However, not all tocotrienols are created equal.
In view of the low bioavailability of tocotrienols, it is very important to choose the right bioenhanced tocotrienol system, such as EVNol SupraBio — not just because of its strong human clinical substantiation, but to ensure the enhanced absorption of tocotrienols into the plasma and the delivery of tocotrienols to the brain and heart for optimum benefits and functions.
The old adage of “you are what you eat” may not apply in dietary supplementation. It should be, in the case of fat-soluble compounds such as tocotrienols: “you are what you absorb.”
Therefore, the long-term consumption of EVNol SupraBio ensures the optimum absorption of tocotrienols and may help you to age gracefully by reducing health conditions such as cognitive decline or heart problems.
