In recent years, greater focus has been placed on studies aimed at verifying and measuring the efficacy of probiotics in the treatment and/or prevention of infections in the lower female urogenital tract. This is especially true for Candida vulvovaginitis and bacterial vaginosis, which are the most common infections found in women of childbearing age. The need for alternative treatments stems from the frequency at which recurrence of such infections is found in clinical practice. Such cases lead to significant psychophysical discomfort for the patient, causing substantial decrease in the quality of life and an increase in health costs.
The failure of antibiotic therapy, which is commonly used in the treatment of these infectious diseases, is linked to two main factors: the development of resistance to drugs by pathogenic microorganisms and the negative impact of antibiotics on vaginal microflora, which impedes regeneration of the lactobacilli that constitute the main line of defense of the vaginal ecosystem for women of childbearing age. The effectiveness of probiotics for treating gastroenterological pathologies has been historically proven by the scientific literature. For gynecology, however, particularly for mycotic and bacterial infections of the lower genital tract, randomised controlled clinical studies are necessary for confirming the efficacy of new probiotic-based formulations.
RESPECTA is a medical device for oral use consisting of a mixture of probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus LMG S29159 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC SD5675 in combination with bovine lactoferrin RCX).
Lactoferrin is a protein that was isolated from bovine milk in 1960. It particularly inhibits the growth of pathogenic germs in the intestine. Thus, lactoferrin has an inhibiting effect on infections since it favors the growth of normal bacterial flora which are not iron-dependent, and it is synergic with the bio-modulating and anti-infective activity of probiotics.
Laboratory data has shown that the lactobacilli contained in RESPECTA have bacteriostatic activity against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria (Bertuccini et al. 2017). It has also demonstrated the ability of bovine lactoferrin RCX to promote biofilm formation by the two lactobacilli in a strain-specific manner (Bertuccini et al. 2018).
A clinical investigation carried out on healthy women (De Alberti et al. 2015) demonstrated the ability of these strains, after oral administration, to migrate from the intestine to the vagina and persist up to 7 days from the last oral intake.
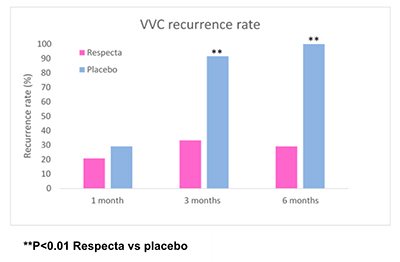
Subsequently, an RCT trial published in 2018 in the Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (Russo et al. 2018) documented the ability of this product, after a single daily intake for 15 consecutive days, to rebalance states of symptomatic vaginal dysbiosis (intermediate Nugent score) with remission of symptoms such as burning and leucorrhoea and normalization of the Nugent score, a microbiological parameter attesting to a state of vaginal eubiosis. Additional recently-published RCTs (Russo et al. 2019a; Russo et al. 2019b) have confirmed the therapeutic efficacy of RESPECTA in the treatment of both bacterial (bacterial vaginosis) and fungal (mycotic vaginitis) recurrent infections. The results, which are not surprising, suggest that administration of RESPECTA during prophylactic or maintenance cycles for a period of at least 10 days during the premenstrual period (in the case of recurrent mycotic vaginitis) or the post-menstrual period (in the case of recurrent bacterial vaginosis) reduces the risk of recurrence of infection (see graph). It also reduces the consumption of azoles or antibiotics (often used for such infections), and therefore represents an undoubtedly efficacious therapeutic aid that will achieve a high rate of compliance by women.
