These findings have global implications for the nutraceutical, ingredient and functional food industries, for healthcare professionals and for the tens of millions of Americans aged 40 and older for whom mitigating age-related muscle loss can have the most impact.
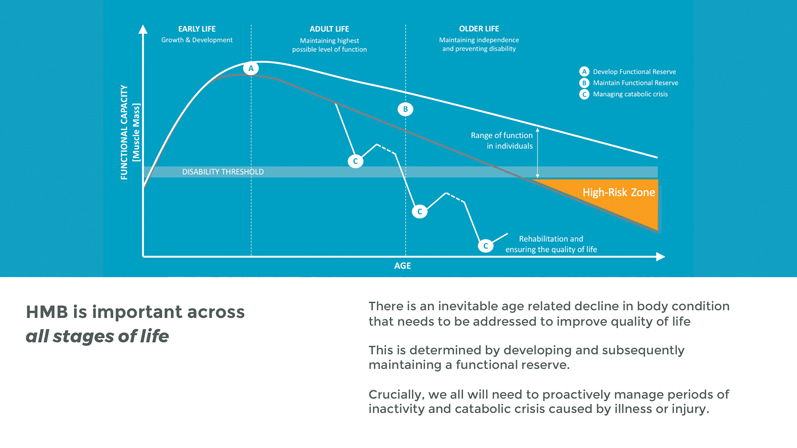
Involuntary age-related muscle loss affects 100% of the 40-plus population, often diminishing quality of life in adults aged 60 or older. After reaching 70 years of age, muscle mass erodes at about 1% per year — increasing the risk of falls and other accidents as well as prolonging the recovery time from injuries and illnesses.
Overall energy and strength decline, along with independence. Education in this area, particularly regarding the importance of exercise to stem natural muscle loss, is paramount for public health.

Larry Kolb
However, a large population of people who wish to address their muscle loss cannot exercise enough to do so (and many Americans do not want to exercise much at all). That is what makes the results of a new study so remarkable: HMB, taken in combination with vitamin D3, improved muscle function in older adults, even without exercise.
The year-long, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), was published in The Journals of Gerontology.1 Its findings suggest that HMB is poised to become the flagship ingredient to attenuate natural muscle loss.
The research
The final study considered 117 healthy adults aged 60 or older who had taken either 3 g of calcium HMB (the most common dosing in HMB studies regarding adult body composition) daily in addition to 2000 IU of vitamin D3, split into two doses, or a placebo supplement.
In each of those groups, half of the subjects participated in a mild resistance training programme of 60-minute supervised progressive resistance training sessions, 3 days a week. The other half did not exercise.
Researchers measured physical function, muscle strength and body composition at 3-month intervals. Participants also completed questionnaires regarding health, quality of life and circumplex affect at each visit. The results indicated that HMB’s long-term functional benefits were fully realised when there is sufficient vitamin D3 present … and that they appeared even among the cohort that did not exercise:
- Exercise was not needed to realise the muscle health benefits of HMB+D. combining HMB+D and moderate resistance training did not provide any further benefit compared with either exercise or HMB+D alone. This indicates that HMB+D may uniquely protect muscle strength and physical function in those who are unable or unwilling to exercise, particularly older adults who are frail and already have age-related muscle loss.
- Among non-exercisers, participants taking HMB+D experienced greater improvements in physical function and tended to have greater increases in strength than did participants taking the placebo supplement.
- HMB+D may also help people feel more energetic: beyond physical benefits, the HMB+D cohort reported increased “high activation” emotions.
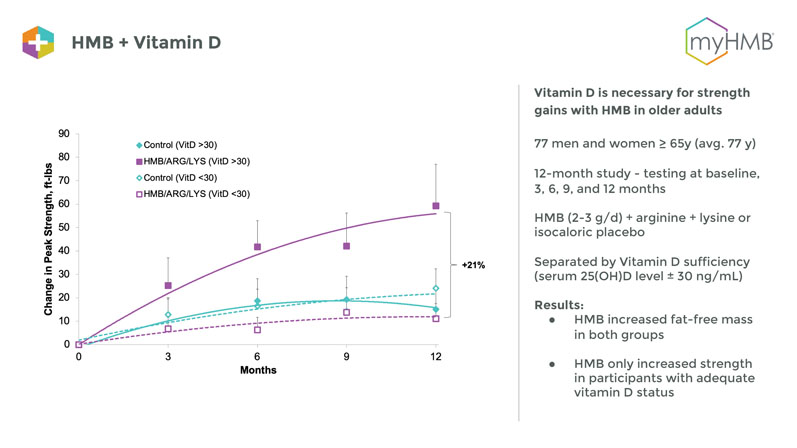
Lisa M. Pitchford, PhD, MTI Biotech, and the senior scientist on the study research team, said that the study was conducted because a recent analysis of HMB found that the ingredient increased lean body mass in adults aged 65 and older but didn’t appear to have a corresponding increase in strength.2
“Because 70% of those study participants had insufficient vitamin D levels, researchers performed a retrospective analysis and found that only those who had sufficient vitamin D3 levels saw an increase in strength with HMB,” Pitchford said.3
“That led to the hypothesis that it is important for older adults to have an adequate vitamin D3 status when supplementing with HMB.”
HMB+D Non-Exercise Group Benefits at 6 Months
• Significant increases in the functional index compared with those observed in the control + no exercise group at 3 (p=0.03), 6 (p=0.04) and 12 months (p =0.04).
• Significant lean body mass benefit within the non-exercise group (0.44 ± 0.27 kg HMB+D vs −0.33 ± 0.28 kg control, p <0.05).
• Improvement in knee extension peak torque (60°/s) was significantly greater in HMB+D-supplemented participants than in the non-supplemented group (p=0.04) at 3 months, 10.9 ± 5.7 Nm and −5.2 ± 5.9 Nm, respectively.
Global implications
There are two very well-established, multibillion-dollar categories in the musculoskeletal space: bone health and joint health. But whereas only some adults will experience health concerns related to their bones or joints, there is now a compelling opportunity to help 100% of adults aged 40 and older to stave off muscle health degradation through nutritional intervention. This represents another potential multibillion-dollar segment.
Four primary markets are poised to benefit from this research: sports nutrition, active adults, adults who want to age healthily and recovery. From a clinical nutrition perspective, recovery crosses all divisions of medicine because it addresses faster muscle recovery and a return to mobility after illness, injury or long periods of inactivity.
Improved muscle health may also help to resolve issues related to perceived fatigue and a generalised lack of energy in older adults.
There is a tremendous need to communicate to adults between 40 and 65 that slowing the decline in muscle mass and function now will significantly improve their ability to maintain their quality of life in their 60s, 70s and beyond.
Easy incorporation into nutraceutical and food applications
Ingredient formulation versatility becomes essential when marketing to such a wide range of age groups. Some older consumers suffer from pill fatigue. Some have wearied of dairy based protein products. Others want to supplement their nutrition without a lot of extra calories.
HMB is a versatile, easy-to-use ingredient. “The beauty of HMB plus vitamin D3 is that it is a very scalable, uniform and flexible compound — it holds up to different conditions including high heat for bars, and it is stable in liquid and powder formats,” said Shawn Baier, VP of Business Development, TSI Innovative Products Division.
“The combination can also be used in RTDs, gummies, shots, pills, softgels and stickpacks. HMB has been used in RTD protein shakes for years.”
Baier added: “Any time you work with an amino acid-like ingredient, there will be bitter notes. However, HMB is not difficult to mask, especially in dairy based products or when combined with lower pH fruit flavours.”
Responsibility for global good
TSI is taking a leadership role in responsibly defining and building the category of age-related muscle loss. This involves identifying the problem for both the trade and consumers, as well as educating them about the risks and opportunities. TSI has travelled around the world to speak with physicians, R&D departments, marketing departments and consumers.
Although HMB’s impressive portfolio of scientific support positions it as the ideal foundational ingredient, TSI’s work is not entirely product-focused. As industry, consumer and healthcare professional awareness of age-related muscle loss increases, doors will open for other ingredient companies to contribute to the field.
TSI is looking for brand partners in key markets around the world to extend its reach to the right consumer demographics. Moving forward, the right team can develop integrated marketing and consumer education programs to extend HMB’s support of this underplayed category.
References
- J.A. Rathmacher, et al., “Long-term Effects of Calcium β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate and Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Muscular Function in Older Adults with and without Resistance Training: A Randomized, Double-blind, Controlled Study,” The Journals of Gerontology: Series A 75(11), 2089–2097 (2020): https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glaa218.
- S. Baier, et al., “Year-Long Changes in Lean Body Mass in Elderly Men and Women Supplemented with a Nutritional Cocktail of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB), Arginine and Lysine,” J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 33, 71–82 (2009): doi:10.1177/0148607108322403.
- J.C. Fuller, Jr, et al., “Vitamin D Status Affects Strength Gains in Older Adults Supplemented with a Combination of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate, Arginine and Lysine: A Cohort Study," J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 35(6), 757–762 (2011): doi:10.1177/0148607111413903.
